Router Components, A router is a networking device that joins two different networks by forwarding data (Internet Protocol) packets from one network to another network and it is also known as IP routing, IP routing is in the form of either unicasting, multicasting and broadcasting.
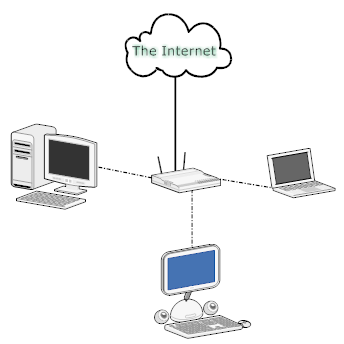
A router consists of two nodes named as source node and destination node, at source node data packets are transferred and destination node receives data packets from source node.
Generally, data packets are forwarded from one router to another router through networks until it reaches destination node and this continuous transformation of data packets from one router to another router forms that constitute an internet work after 192.168.0.1 Admin login.
Here we will discuss about what is a Router?. The main function of a router is to connect two or more networks together and maintaining broadcast traffic under control. There are thousands of companies producing routers such as Linksys, Juniper, Netgear, Nortel, HP, D-Link and Belkin, Redback, Cisco, Lucent, 3-Com, etc…
Every router have a IP address to connect or modify routers settings through web based interference, this IP address will be given to a router while manufacturing that router. A router consists of two types of network named as Local Area Network LAN and Wide Area Network WAN. LAN is internet network limited to a small office, single building, multiple buildings inside a campus and LANs are faster and more secure than WANs.
Why do we need a router?
Here we are explaining about “Why do we need router?” and functions of a routers are given below.
- A router acts as a default gateway.
- The Router does protocol translation.
- Router forwards/moves (route) the data between networks.
- Route data between networks.
- Routers learn and go through loop free paths.
- Router calculates best paths for reaching the network destinations.
Router Components & Parts:

A router is a specialized networking device that transfers data between two or more computers and it have some main parts given below.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Flash Memory.
- Non-Volatile RAM.
- RAM
- Network Interfaces.
- Console
Central Processing Unit:
Central processing unit maintains special software called operating system, in CISCO routers IOS or Cisco operating system will be used and in Juniper routers JunOS will be used. This operating system provides all the networking functions of the router.
Flash Memory:
Flash Memory is Just like hard disk drive in your computer, if you use SSD in your computer then your computer used Flash ram just like as routers. Operating system will store in flash memory routers.
Non-Volatile RAM:
Non-Volatile RAM (Random Access Memory) is an additional memory used to store Operating system and backup. So router is boot form here and also all applications of it boot from Non-Volatile RAM.
RAM (Random Access Memory):
The RAM is a main part of routers and also in computers where the operating system in routers or computers is loaded. RAM is also used for caching routing tables, routing metrics, and ARP tables and data that can speed up the process of packets forwarding. After finishing of routers startup then router starts to calculate its own routes and receives network routes via OSPF, EIGRP, IS-IS and BGP etc… from other routers.
Network Interfaces:
Generally routers have more number of network interference’s, operating system maintains router drivers to access the network hardware in the interface modules.
A router consists of two nodes named as source node and destination node, at source node data packets are transferred and destination node receives data packets from source node, at startup of data packets at source node knows destination node.
Routers will know at which ports as they start up, After that routers learn from other routers they are connected to and then learn which interface to transmit packets on to reach a remote network destination.
Console:
Management of a router and configuring a router will be done at the console of individual devices like as troubleshooting and diagnostics. These are some basic and main components of router.
Conclusion:
In Router Components, there are thousands of data packets or IP packets are transferring to one router to another router per second, routers are not only traffic routes to other networks but also it finds shortest distances and uses it, routers learns this shortest distance by using metric value.
What is the Default IP for Router Admin Login?
The Router has defined their Wifi Router Default Login IP address 192.168.0.1 to login the admin panel, and they have maintained the default IP at their user manuals along with stick a label on the router.
Why do we need a router?
The following are the functions of a router: Routers allow numerous computers to share a single Internet connection from your Internet service provider (Internet Service Provider). This is true whether you’re using a cable, DSL, or a 3G mobile using a USB dongle. Some routers include firewalls that provide significant security against network hacking.
Do I need a router if I have a modem?
No, in a technical sense, but yes in a practical sense. Because a modem can only connect to one device at a time, if you wish to utilise the internet from several devices, you’ll need a router.
Can you get internet without a router?
There’s a popular fallacy that you don’t need a router if you have a simple configuration, such as only one home computer. You may, as you’ve learned, simply plug your computer into your broadband modem and begin browsing the internet.
Can I use just a router?
Yes, it can, but only for creating and managing local networks between your local devices. You can use a router to connect your phone, computer, smart TV, printer, and smart home devices to the Wi-Fi network and share data amongst them. However, a router on its own won’t offer a connection to the internet.