IP Routing is the process during which data packets are forwarded from one node to another node on a network until they reach their destinations from the source. Generally, Routing is the process of learning or choosing a path for traffic in a network. The routing process is applied in many different networks such as Circuit Switched Network, Public Switched Network, and Computer Network, this computer network such as the internet.
When the amount of data is transferred from one machine to another machine on the same network related to IP address, the transferred data is divided into small parts or units called packets. This smaller packet consists of data useful when traveling to their destination, as you know that hundreds and thousands of data packets are transferred from source to destination in a single second, and this because of the fast sorting process in that device.
Switching is the same as IP Routing but switching has very small technical differences, in IP routing IP packets are forwarded from source to destination, and IP learns packet switching in comparison with that circuit switching, The IP Routing protocols give access to create a routers table that helps data packets to reach the final destination.
These protocols include Border Gateway Protocol (BGW), Intermediate system to intermediate system (IS – IS), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Routing Information Protocol (RIP). Generally, in routing, process data packets are forwarded on the basis of routing tables which maintain a set of routes to travel network destinations.
How IP Routing Works:
IP Routing works just like as sending a message data to another person through internet, this messaged data packets passes through lots of routers to reach their destination this process is also known as routing.
Here each data packet carries certain amount of data such as IP address of source and destination location to reach their destination. Generally each router consists of routing table about data of other router or about neighboring router.
Each data packets are travels in different ways and passed through different networks and take different paths based on their routing tables but finally reaches the same. After reaching the destination, the destination address and device address will match. The data packets are taken by the device where the IP module on it will re-assemble them and send final data to TCP for the next step of processing.
TCP/IP:
Transmission Control Protocol TCP and IP work together to check whether the transmission of data is correct or not and to ensure no data packet is lost. And there is no unwanted delay in the transmission of data packets. Sometimes TCP is replaced by User Datagram Protocol (UDP) which does not sure in the transmission of data and just transmits data packets, Some VoIP devices use User Datagram Protocol for making calls and lost packets do not affect the call quality.
Types of IP Routing:
Routing is performed in network layer of a device in order to transfer packets by choosing optimal path to reach destination. There are three types of routing named as
- Static Routing.
- Default Routing.
- Dynamic Routing.
Static IP Routing:
Static routing is the process in which the routing table is manually specified by the network administrator, so in static routing, the network administrator has to modify routing manually. Generally, static routing can be implemented in small networks as dynamic will be implemented in large networks. Static routing provides high security of data transmission between two devices. If there is any link failure in static routing then it obstructs the rerouting. And static routing is also known as non-adoptive routing, this non-adaptive routing enables a pre-computed route to be fed into the routers offline.
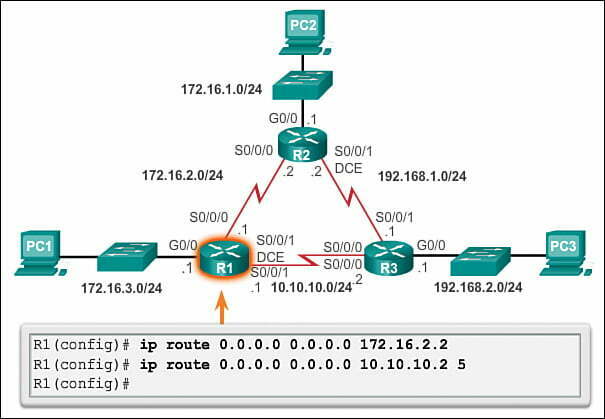
Example for Static route: hostname(config)# route outside 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 [1]
Default IP Routing
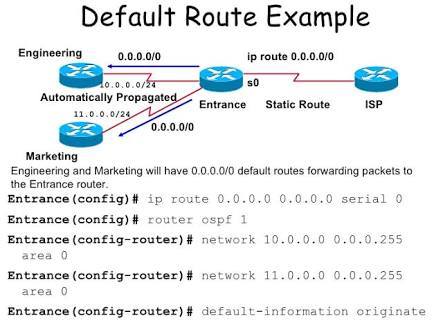
Default routing is a process in which the router is configured to transfer all packets to a single router and it identifies Gate way IP address to which ASA sends all IP packets, a default route is same as static root with 0.0.0.0/0 as destination IP address. Generally, it is used in stub routers which has only one route to reach all other destination networks.
Example for Default route: hostname(config)# route outside 0 0 192.168.2.4
Dynamic IP Routing:
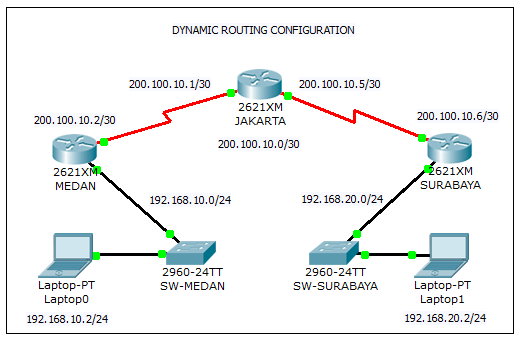
Dynamic routing is the process in which routes are automatically adjusted on the basis of a current state of the route in the routing table. dynamic routing is implemented by using IP Routing Protocols. Dynamic routing uses extra protocols to discover network destinations.
Here Routes are updated according to change in topology and the dynamic route is generally used in large networks as static routing is used in smaller networks. Routing protocols such as RIP, EIGRP, etc are involved in the routing process. So RIP and OSPF is the best examples of dynamic routing.
What is Routing?
Routing is the technique by which your computer sends a packet between subnets. Your computer must forward data packets to a router if you wish to communicate with a machine on a different subnet than your own.
How IP Routing Works?
IP routing is the process of sending data as IP packets from one network to another. Hosts from separate networks are unable to communicate with one another by default. IP routing is used when two hosts on different IP networks desire to interact with each other.
How Many Types in Routing?
We have two types of routing Static and Dynamic. Border routers connect an inner autonomous system to external networks, and routers that connect a statically routed network to a dynamically routed network. On a system, it’s typical to use both static and dynamic routing.
How do I change/Reset the admin username or password of Router device?
The only way to gain access to the web management system if the administrator password is lost or forgotten is to reset the Router settings to factory defaults. To reset the password, the user must push and hold the reset button for at least 20 seconds.